We can talk about Deline from two aspects:one is the post-processing of customized paper products, and the other is design.
Dieline in Custom Manufacturing
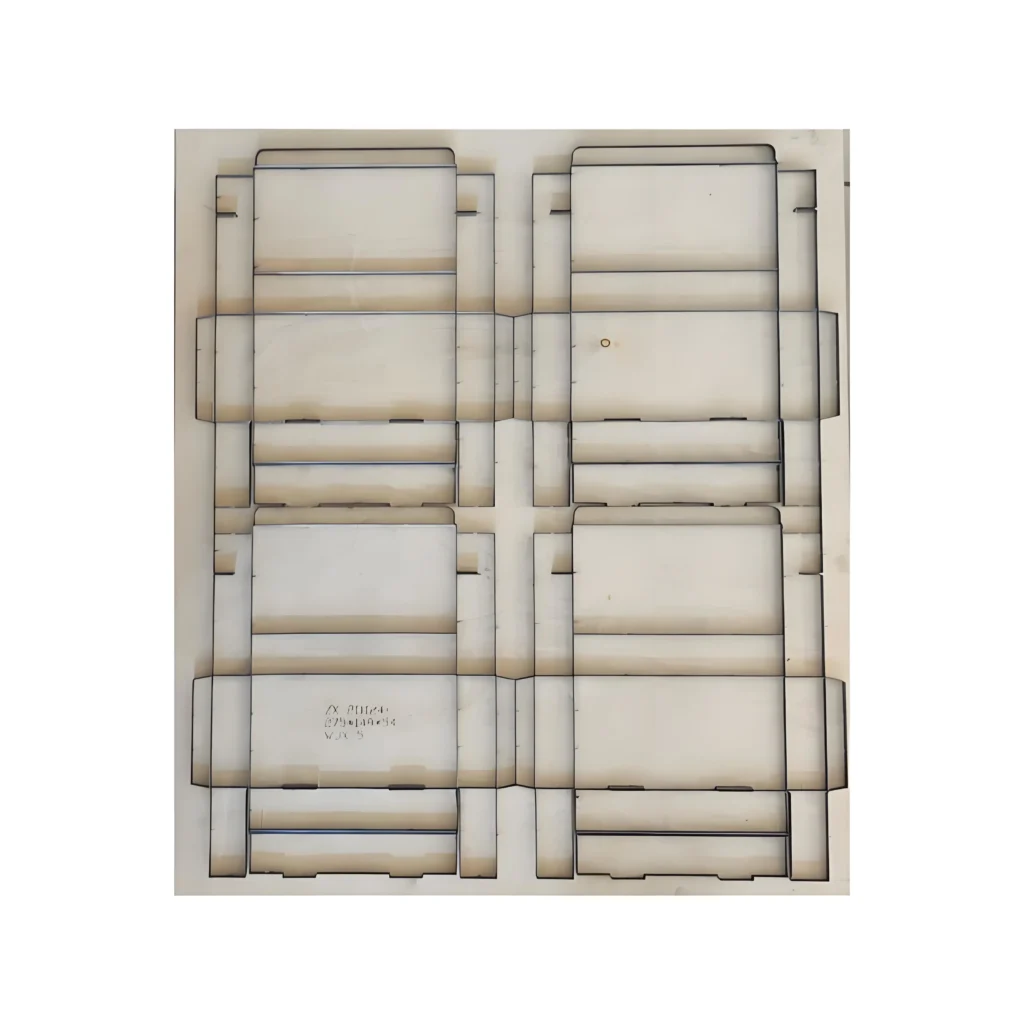
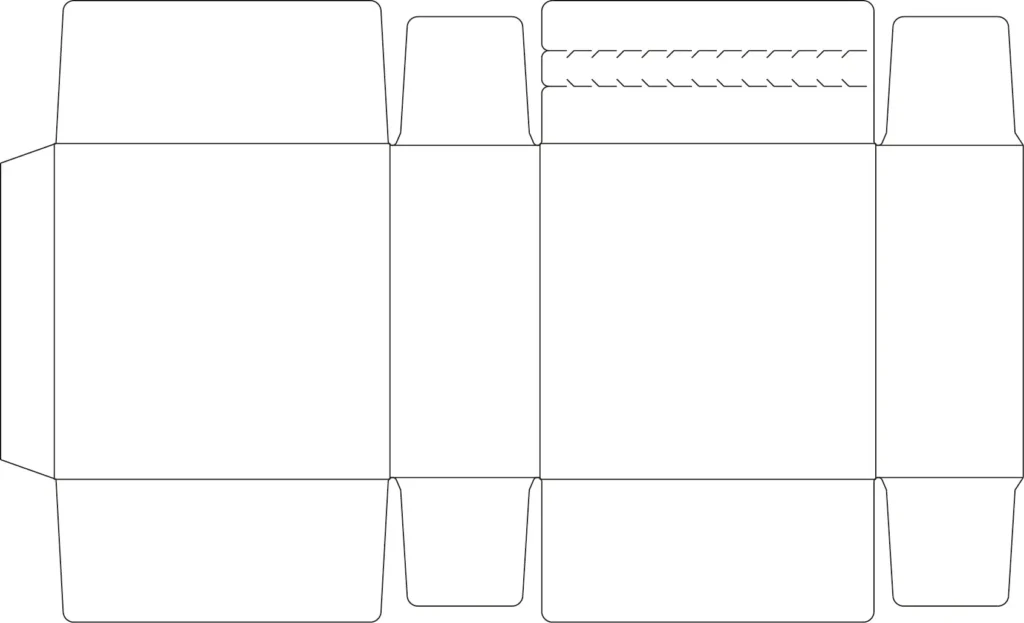
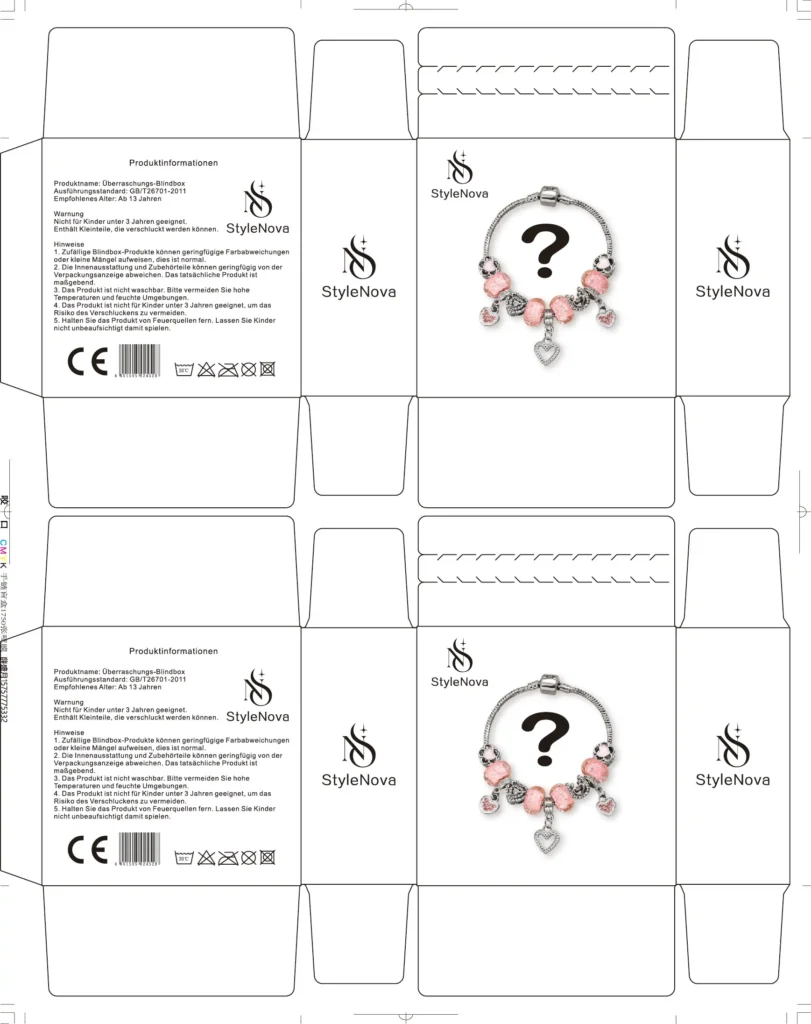
A dieline in custom manufacturing is a template that outlines the precise dimensions, cut lines, folds, and perforations required to create a physical packaging structure. It serves as a blueprint for die-cutting tools, ensuring accurate material shaping during mass production. Manufacturers rely on dielines to optimize material usage, minimize waste, and maintain structural integrity. The design must account for material thickness, assembly tolerances, and production limitations (e.g., machinery capabilities). Prototyping and testing are critical to validate the dieline’s functionality before full-scale production. Collaboration between designers and engineers is essential to balance aesthetic goals with technical feasibility. A well-crafted dieline reduces errors, streamlines workflows, and ensures consistency across batches, directly impacting cost efficiency and product quality.
Dieline in Design
In design, a dieline acts as the foundation for visualizing and arranging graphic elements on packaging. It defines where artwork, logos, text, and functional elements (e.g., glue tabs, folds) will be positioned in 2D before conversion into 3D. Designers use dielines to ensure brand consistency, readability, and visual appeal while adhering to structural constraints. Software like Adobe Illustrator is used to layer graphics over the dieline, aligning them with cut/crease lines. Considerations include bleed areas, safe zones, and substrate limitations (e.g., printability of certain materials). A strong dieline harmonizes form and function—enhancing user experience (e.g., easy opening) and protecting contents. Iterative revisions with manufacturers ensure the final design is both aesthetically compelling and producible, bridging creativity and practicality.